Windows 11, introduced by Microsoft a few years ago, brought a slew of new features and changes, along with heightened system requirements. One of these requirements, the need for a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) hardware chip, has frustrated users attempting to upgrade. Even when a TPM hardware chip is present on the motherboard, some users encounter a vexing ‘TPM Device Not Detected’ error.
If you’re eager to try Windows 11 but find yourself unable to do so due to this error, this guide will help you understand why the issue occurs and how to resolve it.
Understanding TPM:
Firstly, let’s comprehend what TPM is and its significance. Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a hardware chipset embedded on your PC or laptop’s motherboard. It serves as an international standard for secure cryptoprocessing. TPM primarily focuses on security, providing hardware-level protection and enabling encryption of disks using Windows security features like BitLocker and Windows Hello PIN. For Windows 11, having TPM 1.2 or 2.0 is mandatory to ensure proper security and system functionality.
Fixing the ‘TPM Device Not Detected’ Error:
Now that you grasp the importance of TPM, here are the best methods to resolve the ‘TPM Device Not Detected’ error on your Windows 10 computer and proceed with installing Windows 11.
1. Verify TPM Chip Presence:
Start by confirming whether your motherboard and CPU have an integrated TPM chipset. If your system lacks a TPM chip, you won’t be able to resolve the error. Check your motherboard and CPU specifications online to ensure TPM 2.0 is officially listed as part of the device specifications.
2. Check TPM Status in BIOS:
Even if your PC has TPM, encountering the ‘TPM device not detected’ error could indicate that TPM is disabled in the BIOS. To rectify this, access your system’s BIOS and ensure TPM is enabled. Enabling TPM in BIOS can be a complex task, varying based on your motherboard’s brand and model. You can refer to online resources such as YouTube videos or your motherboard manual for specific instructions on enabling TPM in BIOS.
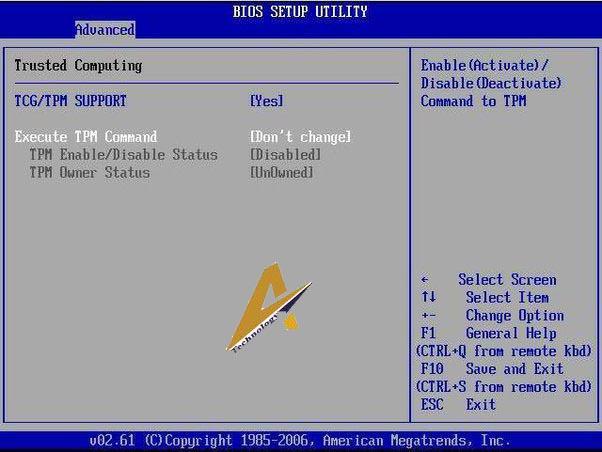
If you prefer a step-by-step guide, you can follow our tutorial on How to Enable TPM 2.0 in Windows PC.
3. Update BIOS or UEFI:
If TPM is already enabled in the BIOS, yet the error persists, updating the BIOS or UEFI firmware might be necessary. BIOS updates, however, require caution as incorrect settings can cause serious issues. To update the BIOS safely, follow these steps:
- Disable Bitlocker device encryption.
- Visit the official website of your PC’s manufacturer.
- Download the latest BIOS firmware for your specific PC model.
- Run the downloaded installer and follow on-screen instructions to update the BIOS.
Alternatively, for those uncomfortable with updating BIOS on their own, consider taking your PC or laptop to the nearest service center for professional assistance. This ensures a secure and error-free update of the BIOS/UEFI firmware.
4. Reinstall TPM Driver:
If TPM 2.0 appears in your Device Manager but the error persists, you can try reinstalling the TPM driver. Follow these steps:
- Click on Windows Search and type “Device Manager.” Open the Device Manager from the search results.
- In Device Manager, expand the ‘Security Devices’ section.
- Right-click on ‘Trusted Platform Module’ and select ‘Uninstall Device.’
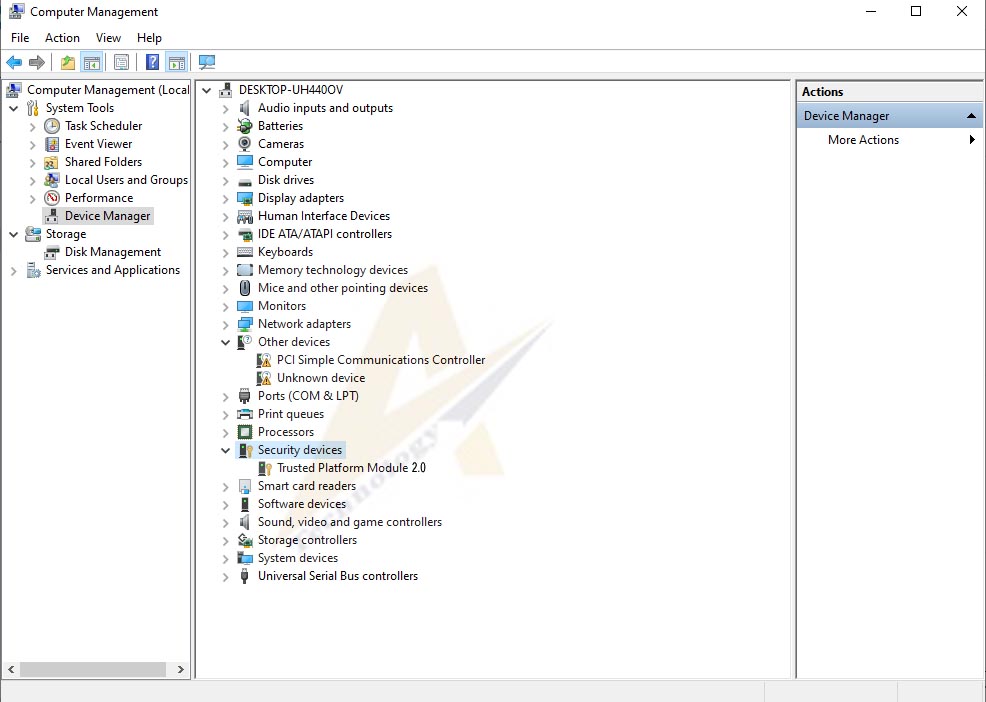
- Confirm the uninstallation when prompted.
- Restart your computer.
5. Reset BIOS Settings by Unplugging the Battery/CMOS:
Resetting the PC BIOS can often resolve persistent issues. For laptops, power down the device and remove the battery. Desktop users, on the other hand, should open the CPU cabinet and locate the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor). CMOS is the term used to describe the memory on a computer motherboard that stores the BIOS settings. By removing the CMOS battery (only if you have technical expertise), all BIOS settings are wiped, allowing for a reset to default configurations.
6. Bypass Windows 11 TPM Requirements:
If you wish to enable TPM for Windows 11 installation, there’s a method to bypass Windows 11’s TPM requirement. This approach involves using third-party applications.
Explore the options available in our guide, How to Bypass Windows 11 TPM Requirement, to find suitable third-party apps. Alternatively, a simpler method is to create a Bootable USB drive using the Rufus utility.
Rufus offers an option to eliminate the Secure Boot and TPM 2.0 requirements. To utilize Rufus for bypassing Windows 11 requirements, refer to our guide, How to Create a Bootable USB to Bypass Windows 11 Restrictions.
By following these methods, you can potentially resolve the ‘TPM Device Not Detected’ error. If your PC has a TPM chip and you’ve attempted all these solutions, the issue should have been addressed. Please inform us which method proved effective in fixing the Windows 11 TPM error.




